import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from simtk import unit
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
/tmp/ipykernel_3880/3492738578.py in <module>
1 import numpy as np
----> 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 from simtk import unit
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'matplotlib'
Langevin
To easily run tests with langevin dynamics, the method simulations.langevin_NVT provides a simple interface. Let’s first of all see a simple example on how to use it:
from uibcdf_test_systems.simulation import langevin_NVT
from uibcdf_test_systems import FreeParticle
free_particle = FreeParticle(n_particles=1, mass=10*unit.amu)
initial_positions = np.zeros((1,3),dtype=float)*unit.nanometers
initial_velocities = np.zeros((1,3),dtype=float)*unit.nanometers/unit.picometers
time, position, velocity, kinetic_energy, potential_energy = langevin_NVT(system=free_particle.system, temperature=300*unit.kelvin,
friction=1.0/unit.picoseconds, initial_positions=initial_positions,
initial_velocities=initial_velocities, integration_timestep=0.1*unit.picoseconds,
saving_timestep=1.0*unit.picoseconds, total_time=0.5*unit.nanoseconds)
Every method in the module simulation has at least five possible output arguments: time, position, velocity, kinetic_energy and potential_energy.
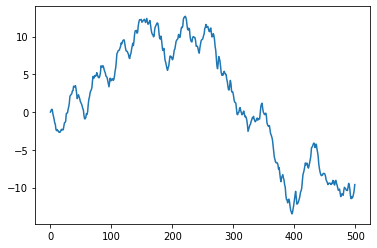
plt.plot(time, position[:,0,0])
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f15fe60f8d0>]
# %load ../../uibcdf_test_systems/simulation/langevin_NVT.py
def langevin_NVT(system, temperature=None, friction=None,
initial_positions=None, initial_velocities=None, integration_timestep=None,
saving_timestep=None, total_time=None, platform_name='CPU', verbose=True):
from simtk.openmm import LangevinIntegrator, Platform, Context
from simtk import unit
import numpy as np
# System parameters.
n_particles = system.getNumParticles()
# Integration parameters.
steps_per_cicle = int(round(saving_timestep/integration_timestep))
n_steps = int(round(total_time/integration_timestep))
n_cicles = int(round(n_steps/steps_per_cicle))
# Integrator.
integrator = LangevinIntegrator(temperature, friction, integration_timestep)
# Platform.
platform = Platform.getPlatformByName(platform_name)
# Context.
context = Context(system, integrator, platform)
context.setPositions(initial_positions)
context.setVelocities(initial_velocities)
# Reporter arrays: time, position, velocity, kinetic_energy, potential_energy
time = np.zeros([n_cicles], np.float32) * unit.picoseconds
position = np.zeros([n_cicles, n_particles, 3], np.float32) * unit.nanometers
velocity = np.zeros([n_cicles, n_particles, 3], np.float32) * unit.nanometers/unit.picosecond
kinetic_energy = np.zeros([n_cicles, n_particles, 3], np.float32) * unit.kilocalories_per_mole
potential_energy = np.zeros([n_cicles, n_particles, 3], np.float32) * unit.kilocalories_per_mole
# Initial context in reporters
state = context.getState(getPositions=True, getVelocities=True, getEnergy=True)
time[0] = state.getTime()
position[0] = state.getPositions()
velocity[0] = state.getVelocities()
kinetic_energy[0] = state.getKineticEnergy()
potential_energy[0] = state.getPotentialEnergy()
# Integration loop saving every cicle steps
for ii in range(1, n_cicles):
context.getIntegrator().step(steps_per_cicle)
state = context.getState(getPositions=True, getVelocities=True, getEnergy=True)
time[ii] = state.getTime()
position[ii] = state.getPositions()
velocity[ii] = state.getVelocities()
kinetic_energy[ii] = state.getKineticEnergy()
potential_energy[ii] = state.getPotentialEnergy()
return time, position, velocity, kinetic_energy, potential_energy
